How to Increase Your Income & Save More
August 9, 2025
Saving Strategies for Financial Stability and Growth
August 9, 2025
What is Personal Finance? A Complete Guide
August 10, 2025
A Guide to Maximizing Savings and Financial Success
August 10, 2025
How to Achieve Financial Success by Avoiding Lifestyle Inflation
August 10, 2025
Wealth Accumulation: Building a Secure Future
August 10, 2025
Stock Market Insights: Navigating the World of Investing
August 9, 2025
Smart Strategies for Managing Unexpected Money
August 9, 2025
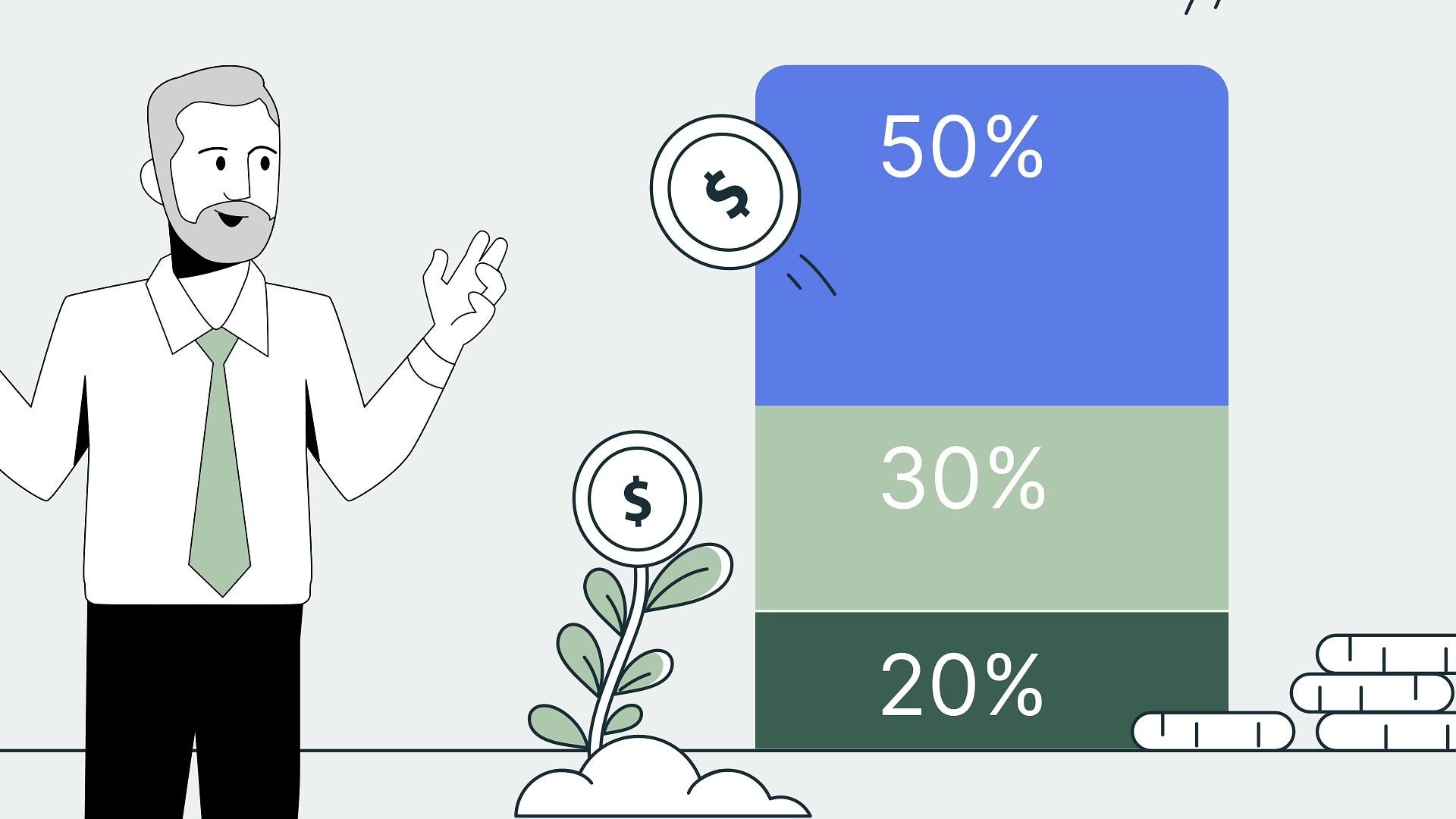
How to Follow the 50/30/20 Rule for Financial Success
August 9, 2025
Set Specific Savings Goals: The Key to Financial Success
August 9, 2025
Saving Strategies for Financial Stability and Growth
August 9, 2025
Pay Yourself First: The Smart Way to Automate Savings
August 9, 2025